
About BBJ
BioBank Japan (BBJ) was established in 2003 at the Institute of Medical Science, the University of Tokyo, as a national project supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Its goal is to advance personalized medicine using genetic information unique to each individual.
From 2003 to 2017, BBJ collected biological samples and clinical information from approximately 270,000 collaborating patients through cooperating medical institutions nationwide. These samples are securely stored in robust storage facilities under the strictest security measures.
To ensure privacy, all personal identifiers such as names, addresses, and dates of birth are removed and replaced with anonymized ID numbers. The de-identified samples and information are then made available to researchers in academic research institutions and private companies under strict compliance with applicable laws, regulations and guidelines. This initiative supports genomic medicine advancements and the development of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
– Start of one of the world’s largest disease biobank projects
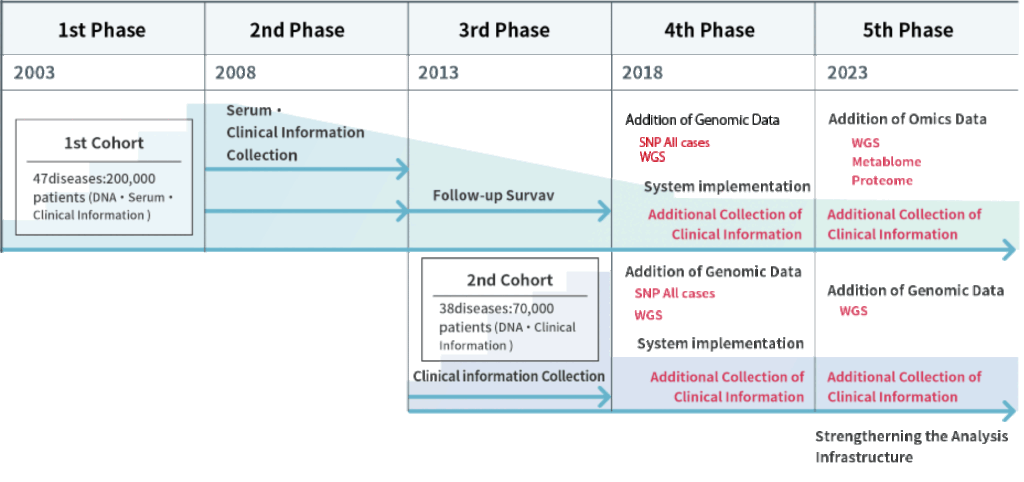
The BBJ was established aiming to develop an infrastructure for the realization of personalized medicine by collecting biological samples (DNA/serum) and clinical information from 200,000 collaborating patients (300,000 cases) with 47 diseases through cooperating medical institutions nationwide, forming the first cohort. The genetic analysis of DNA samples was conducted.
– Expansion with more samples and information
Stable maintenance and operation of the biobank by further collecting samples, clinical information and prognostic information toward utilization of the first cohort’s samples and information. Serum samples were collected once a year from the collaborating patients visiting cooperating medical institutions.
– Growing scale with the cooperation of 67,000 new collaborators
We continued to collect clinical and prognostic information, conduct genomic analysis, and disclose data of the first cohort to promote its utilization. Furthermore, we established a second cohort by collecting blood (DNA) and clinical information from 67,000 (100,000 cases)new collaborators. In 2014 we built an additional serum/plasma storage facility and a new tissue bank. In 2015 we started storing samples provided by cancer clinical research groups in Japan.
– Growth to 267,000 collaborators and 51 diseases; converting samples into data
We promoted utilization of the DNA, serum, and clinical information of a total of 267,000 collaborators with 51 diseases (440,000 cases) in the first and second cohorts, as well as the conversion of biological samples into data to entrench the BBJ as a much-used biobank.
– Toward the further utilization of samples and data
We are promoting the use of samples, clinical information, and genomic data by researchers in both industry and academia by fostering collaboration, establishing infrastructure for genomic and other omics analysis and advancing transformation through digital technology. Also, a system enabling a direct interaction with collaborators is under developpment.